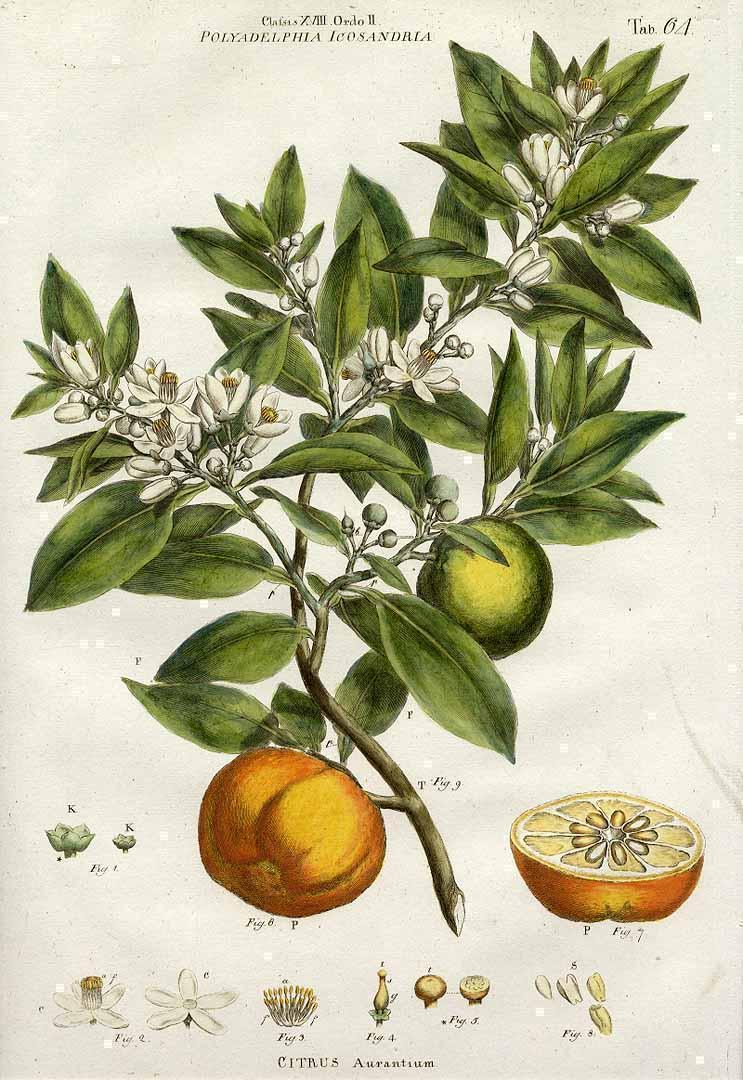
Citrus × aurantium L.
RutaceaeEl naranjo es el árbol con más presencia en el Real Alcázar y en la propia ciudad de Sevilla, donde hay registrados unos 40.000 ejemplares. Asociado al paraíso en numerosas culturas, para los clásicos griegos y romanos la fruta del naranjo serían las mismas manzanas de oro (aurantium significa “de color dorado”) que Hércules robó del Jardín de las Hespérides.
La presencia definitiva del naranjo en el sur de Europa está vinculada a la llegada de los árabes, quienes lo introdujeron especialmente por su valor ornamental, dado el perfume de su flor, el azahar. Los reyes musulmanes de al-Andalus lo usaron en la composición de patios donde los cuatro ángulos del mismo estaban rehundidos y en cuyos parterres se sembraron naranjos, de modo que al pasar por los andenes altos se podían recolectar sus frutos y oler de cerca sus flores. Así, el Patio de las Doncellas del Alcázar fue construido por el rey-sultán don Pedro siguiendo ese modelo de jardín islámico. En los jardines del Alcázar además, junto al llamado Pabellón de Carlos V, existe un naranjo que según la tradición fue plantado por don Pedro, hace 600 años.
La Huerta de la Alcoba del Alcázar fue, durante mucho tiempo, un auténtico bosque de naranjos donde no penetraba el sol, en palabras del veneciano Andrea Navagero en su visita al Alcázar por motivo de la boda de Carlos I e Isabel de Portugal, en 1526. La mayor parte de la producción de cítricos de esas huertas se exportaba a los países del norte de Europa, principalmente a Inglaterra, para la elaboración de mermeladas. La identificación de la naranja amarga con la ciudad es tal que el fruto en los países anglófonos es conocido como Seville orange – naranja de Sevilla.
Consigue el mapa con semillas de Naranjo: tienda R.A
Procedencia
Oriental/AsiáticoCalendario
Hábitat
Morfología
 Árbol
Árbol
 Esférica
Esférica
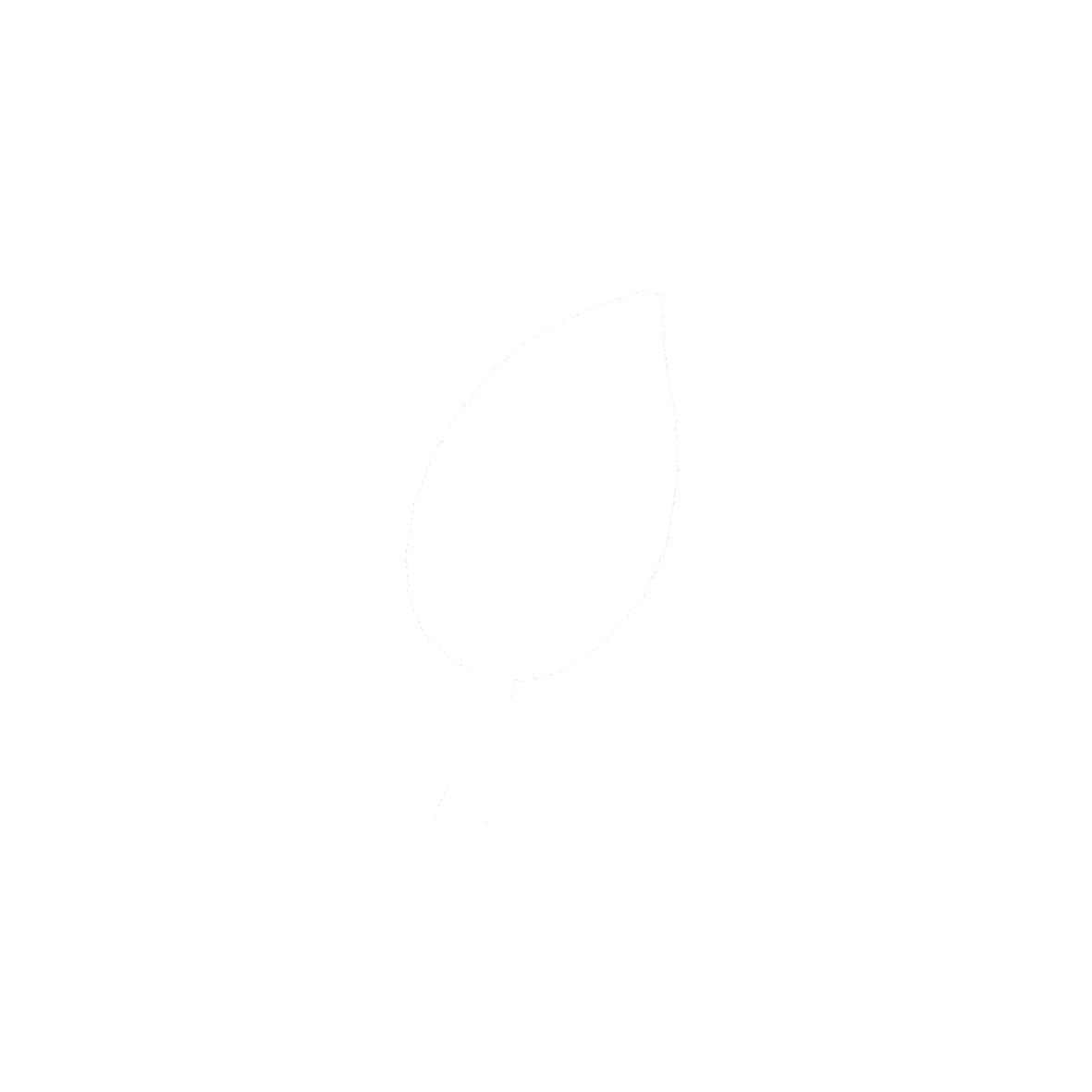 Simple
Simple
 Ovada
Ovada
 Elíptica
Elíptica
 Alterna
Alterna
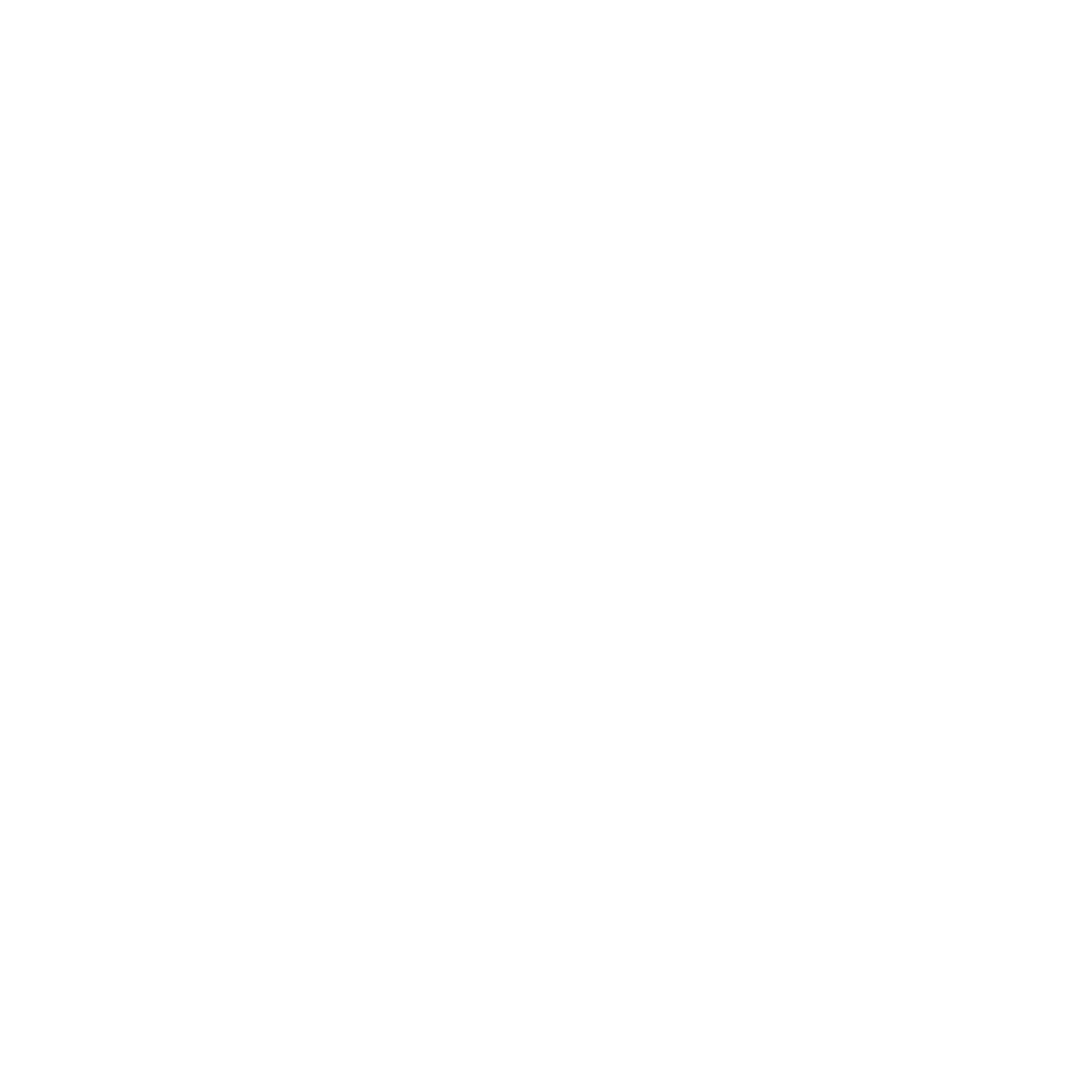 Ondulado
Ondulado
 Entero
Entero
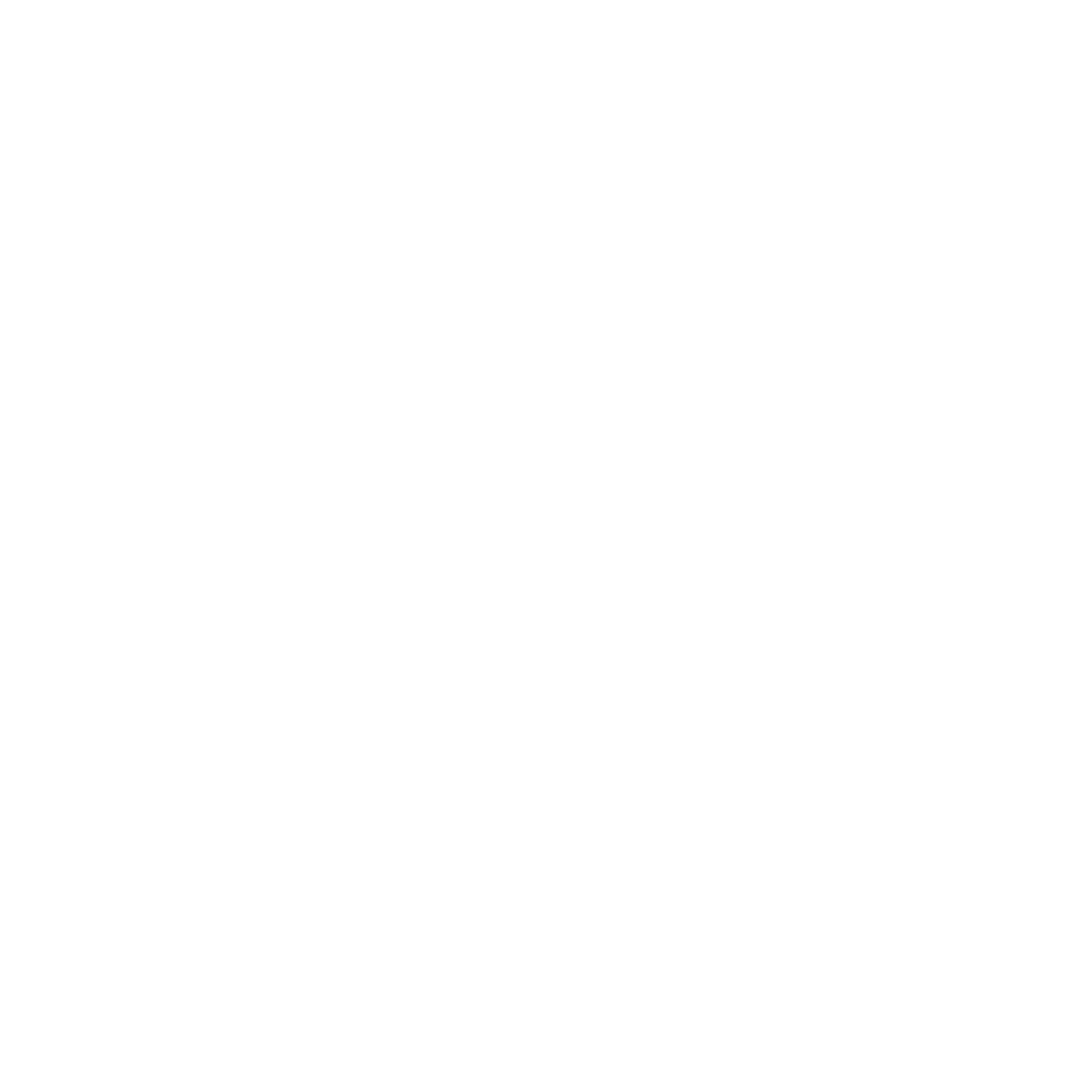 Cuneada
Cuneada
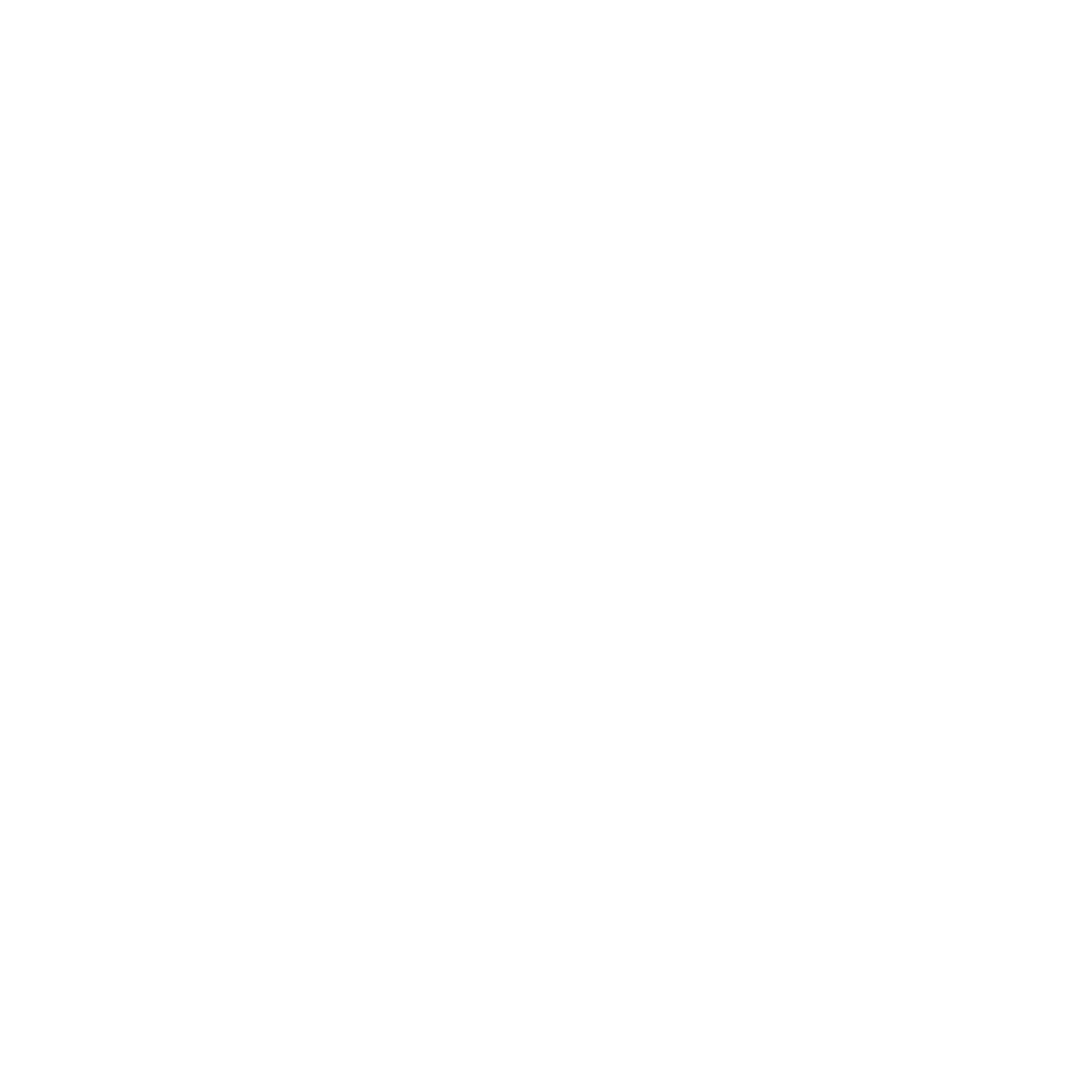 Obtusa
Obtusa
 Acuminado
Acuminado
 Agudo
Agudo
 Perenne
Perenne
